In today’s digital landscape, where data rules and agility are key, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. It’s like having a virtual powerhouse at your fingertips, ready to store, process, and deliver your data at lightning speed. If you are excited to know more about cloud computing, then you are in the right place, so read this article till the end;
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is a transformative paradigm that has revolutionized how businesses and individuals access and manage computing resources. At its core, cloud computing delivers a wide range of services, including storage, processing power, networking, and software, over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. This shift eliminates the need for organizations to maintain physical hardware and infrastructure on-premises, instead leveraging remote servers and data centers operated by third-party providers. Cloud computing encompasses various service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), each offering distinct benefits and capabilities. Additionally, deployment models such as public, private, and hybrid clouds allow organizations to choose the right environment for their needs. Despite the numerous benefits of cloud computing, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and agility, it also presents challenges such as security concerns, vendor lock-in, and integration complexity. By understanding these complexities and considerations, businesses can harness the power of cloud computing to drive innovation, efficiency, and growth in today’s digital landscape.
How does cloud computing work?

Cloud computing works by leveraging remote servers and data centers to deliver computing services over the internet. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it operates:
Infrastructure: Cloud computing relies on a vast network of servers and data centers, owned and maintained by cloud service providers (CSPs) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). These data centers are equipped with high-performance hardware and networking equipment to handle large volumes of data and computing tasks.
Virtualization: Within these data centers, virtualization technology plays a crucial role. Virtualization allows a single physical server to be partitioned into multiple virtual machines (VMs) or containers. Each VM or container runs its operating system and applications independently while sharing the underlying physical resources.
Service Models: Cloud computing offers different service models to meet various needs:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet. Users control these resources’ operating systems, applications, and development frameworks.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud, including operating systems, middleware, and development tools. Developers can build, test, and deploy applications without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers applications and software over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access these applications through a web browser or API, without the need for installation or maintenance.
Access and Connectivity: Users use standard protocols and interfaces to access cloud services through the internet. Whether it’s storage, computing power, or applications, users can provision and manage resources through web-based consoles, command-line interfaces (CLIs), or application programming interfaces (APIs).
Scalability and Elasticity: One of the key advantages of cloud computing is its ability to scale resources dynamically to meet changing demand. Cloud providers offer scalability by allowing users to quickly allocate additional resources when needed and de-provision them when demand decreases. This elasticity ensures optimal performance and cost efficiency.
Security and Compliance: Cloud providers implement robust security measures to protect data and resources in their data centers. This includes encryption, access controls, intrusion detection, and regular security audits. Cloud services often comply with industry standards and regulations to ensure data privacy and regulatory compliance.
Future technologies of Cloud Computing in this upcoming era
The future of cloud computing is poised to be shaped by several emerging technologies that promise to further enhance scalability, agility, security, and efficiency. Here are some of the key technologies expected to drive the evolution of cloud computing in the upcoming era:
Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency, and enabling real-time processing and decision-making. By distributing computing resources to the network edge, edge computing complements traditional cloud architectures, particularly for applications requiring low latency and high bandwidth, such as Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality.
5G Networks: The rollout of 5G networks promises to revolutionize connectivity by delivering faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity. 5G networks will enable new use cases and applications that rely on real-time data processing and high-bandwidth communication, such as autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and immersive gaming. Cloud providers invest in 5G infrastructure and services to support these emerging applications and workloads.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing abstracts away the management of servers and infrastructure, allowing developers to focus on writing code and building applications without worrying about provisioning, scaling, or managing servers. Serverless platforms, such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions offer a pay-as-you-go model where users pay only for the compute resources consumed during execution, leading to cost savings and greater efficiency.
AI and Machine Learning: Cloud providers invest heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities to enable businesses to build and deploy intelligent applications and services. AI and ML technologies are being integrated into cloud platforms to offer services such as natural language processing, computer vision, predictive analytics, and recommendation engines. These capabilities empower organizations to derive insights from data, automate processes, and deliver personalized experiences to users.
Blockchain: Blockchain technology, best known for its role in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is increasingly being adopted for a wide range of applications beyond finance, including supply chain management, healthcare, and identity verification. Cloud providers are exploring ways to integrate blockchain into their platforms to offer services such as secure and transparent transaction processing, decentralized identity management, and tamper-proof data storage.
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing can revolutionize computing by performing complex calculations and solving problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. While still in the early stages of development, quantum computing has the potential to tackle challenges in areas such as cryptography, optimization, and drug discovery. Cloud providers are investing in quantum computing research and offering quantum computing services to researchers and developers to explore and experiment with this groundbreaking technology.
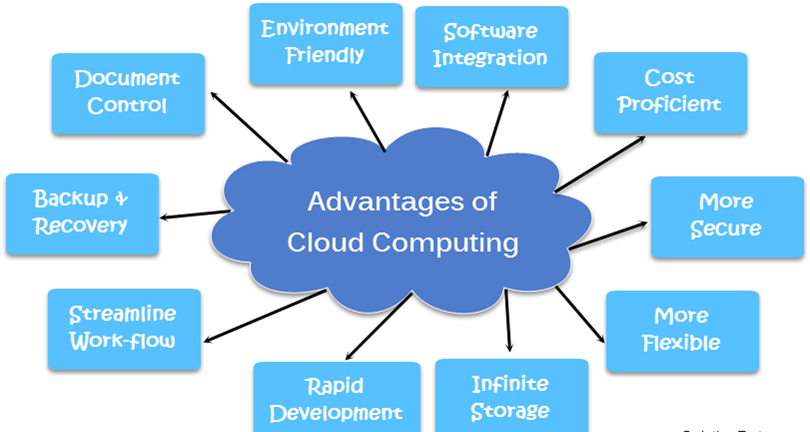
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers many advantages, revolutionizing how businesses operate and individuals access computing resources. Here are some of the key advantages of cloud computing:
Cost Savings: Cost savings are one of the most significant benefits of cloud computing. By leveraging cloud services, businesses can avoid upfront capital investments in hardware and infrastructure. Instead, they pay for computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing for greater flexibility and cost control. Additionally, cloud computing eliminates the need for ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and operational expenses associated with managing on-premises infrastructure.
Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their computing resources up or down according to demand. Whether it’s increasing storage capacity, adding computing power, or deploying new applications, cloud providers offer on-demand scalability to accommodate fluctuating workloads. This scalability ensures optimal performance and resource utilization without the need for overprovisioning or underutilization of resources.
Accessibility and Mobility: With cloud computing, data and applications are accessible from any location with an internet connection. This accessibility fosters mobility and collaboration among distributed teams, allowing employees to work remotely and access critical resources. Cloud-based applications can be accessed from various devices, including laptops, smartphones, and tablets, enabling seamless productivity and flexibility.
Reliability and High Availability: Cloud providers operate redundant and geographically distributed data centers, ensuring high availability and reliability of services. By leveraging redundant infrastructure and automatic failover mechanisms, cloud computing minimizes the risk of downtime and service disruptions. This reliability is crucial for mission-critical applications and businesses operating in competitive, fast-paced environments.
Security and Compliance: Cloud providers invest heavily in robust security measures to protect data and resources in their data centers. These security measures include encryption, access controls, intrusion detection, and regular security audits. Additionally, cloud services often comply with industry standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, ensuring data privacy and regulatory compliance for businesses in various sectors.
Innovation and Time-to-Market: Cloud computing enables businesses to rapidly innovate and iterate on applications and services. By providing access to a wide range of advanced technologies and services, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics, cloud providers empower businesses to experiment, prototype, and deploy new solutions quickly. This agility and innovation accelerate time-to-market and give businesses a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Environmental Sustainability: Cloud computing offers environmental benefits by reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional on-premises infrastructure. Cloud providers can achieve greater energy efficiency and environmental sustainability by consolidating computing resources in centralized data centers and optimizing resource utilization. Additionally, cloud providers are increasingly investing in renewable energy sources and carbon offset programs to further reduce their environmental impact.
How can we build our career in Cloud Computing?
Building a career in cloud computing can be an exciting and rewarding journey, given the growing demand for cloud skills in the IT industry. Here are some steps you can take to kickstart and advance your career in cloud computing:
Gain Relevant Knowledge and Skills:
- Start by acquiring a strong foundation in cloud computing concepts, principles, and technologies.
- Familiarize yourself with popular cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Learn about key cloud services, deployment models, security best practices, and emerging trends in cloud computing.
Earn Certifications: Cloud certifications validate your expertise and proficiency in specific cloud platforms and technologies, making you more competitive in the job market. Consider earning certifications such as AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator, Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect, or CompTIA Cloud+ to demonstrate your skills and knowledge to potential employers.
Hands-on Experience:
- Gain practical experience by working on real-world cloud projects and scenarios.
- Experiment with deploying and managing cloud resources, configuring networking and security settings, and optimizing performance and cost.
- Leverage cloud platforms’ free-tier offerings, labs, and sandbox environments to build and test your skills in a risk-free environment.
Continuous Learning and Development: Cloud computing is a rapidly evolving field, so it’s essential to stay updated on the latest technologies, best practices, and industry trends. Invest time in continuous learning through online courses, tutorials, webinars, workshops, and professional networking events. Engage with online communities, forums, and user groups to exchange knowledge and learn from peers and experts in the field.
Specialize and Differentiate: Based on your interests, strengths, and career goals, consider specializing in specific areas of cloud computing. Whether it’s cloud architecture, DevOps, cybersecurity, data analytics, or machine learning, acquiring specialized skills can set you apart from other candidates and open up niche career opportunities. Tailor your learning and certification paths to align with your chosen specialization.
Build a Professional Network: Networking is crucial for advancing your career in cloud computing. Join professional organizations, attend industry conferences, and participate in local meetups and events to connect with peers, mentors, and potential employers. Actively engage with your network on social media platforms like LinkedIn, sharing insights, contributing to discussions, and seeking advice and opportunities.
Seek Career Opportunities:
- Once you’ve acquired the necessary knowledge, skills, and certifications, start exploring career opportunities in cloud computing.
- Look for job openings in cloud-related roles such as cloud architect, cloud engineer, cloud administrator, DevOps engineer, solutions architect, or cloud consultant.
- Tailor your resume and cover letter to highlight your relevant experience, skills, and certifications, and prepare for interviews by practicing common technical and behavioral questions.
Stay Agile and Adaptive:
- Embrace agility and adaptability in your career journey as the landscape of cloud computing evolves.
- Be open to learning new technologies, exploring different roles, and seizing opportunities for growth and advancement.
- Continuously assess your career goals and aspirations, and make strategic decisions to steer your career in the direction that aligns with your interests and ambitions.
Cloud computing represents a transformative force in the world of technology, offering many advantages for businesses, individuals, and developers alike. From cost savings and scalability to accessibility, reliability, and innovation, cloud computing has revolutionized how we store, process, and access data and applications. As emerging technologies such as edge computing, 5G networks, serverless computing, AI, and blockchain continue to shape the future of cloud computing, professionals have abundant opportunities to build rewarding careers in this dynamic field. By acquiring relevant knowledge, skills, and certifications, gaining practical experience, and staying agile and adaptive, individuals can position themselves for success and make meaningful contributions to the ongoing evolution of cloud computing. As the demand for cloud skills continues to grow, now is the time to embark on the journey and seize the vast potential that cloud computing offers for innovation, growth, and transformation in the digital age.