In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cloud computing networks have emerged as a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure. Offering unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and efficiency, cloud computing networks are revolutionizing the way businesses deploy, manage, and utilize computing resources. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the intricacies of cloud computing networks, from their fundamental principles to their transformative impact on industries worldwide.
Understanding Cloud Computing Networks
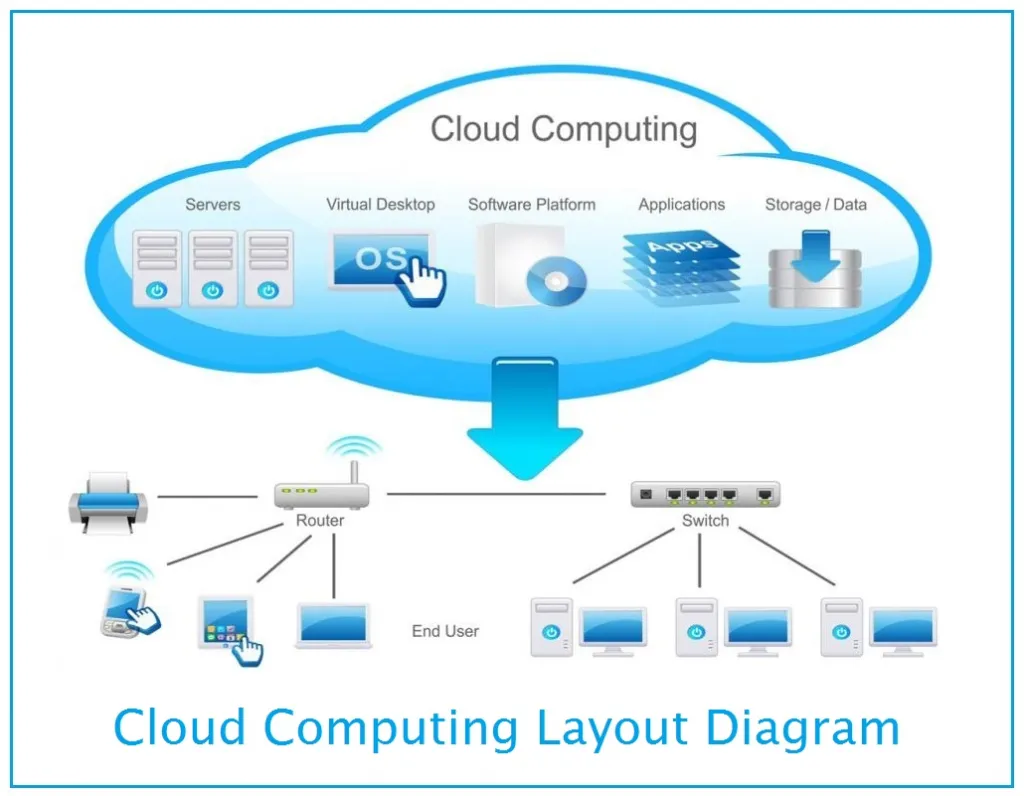
At its core, cloud computing involves the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet, commonly referred to as “the cloud.” Cloud computing networks provide users with access to a shared pool of computing resources that can be rapidly provisioned and scaled on demand. This model eliminates the need for organizations to invest in and maintain costly on-premises infrastructure, instead allowing them to leverage the resources of cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Components of Cloud Computing Networks
Cloud computing networks comprise several key components that work together to deliver computing services efficiently and reliably:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS providers offer virtualized computing resources, including virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure, allowing users to deploy and manage their applications and workloads in the cloud.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offerings provide developers with tools, frameworks, and runtime environments for building, deploying, and managing applications without the complexity of managing underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS applications are fully hosted and managed by cloud providers, enabling users to access software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, without the need for installation or maintenance.
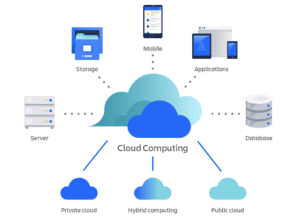
- Public Cloud: Public cloud services are accessible to users over the internet and are shared among multiple tenants. Public cloud offerings are highly scalable and cost-effective, making them ideal for startups, small businesses, and enterprises alike.
- Private Cloud: Private cloud environments are dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted either on-premises or by a third-party cloud provider. Private clouds offer enhanced security, control, and customization options compared to public clouds.
- Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud architectures combine public and private cloud resources, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both deployment models. Hybrid clouds enable seamless data and workload migration between on-premises and cloud environments.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud strategies involve using multiple cloud service providers to meet different business requirements and avoid vendor lock-in. Multi-cloud architectures offer redundancy, resilience, and flexibility by distributing workloads across multiple cloud platforms.
Benefits of Cloud Computing Networks
The adoption of cloud computing networks offers numerous benefits for businesses of all sizes and industries:
- Scalability: Cloud computing networks enable organizations to scale computing resources up or down based on demand, allowing them to accommodate fluctuating workloads and support business growth without the need for significant upfront investments in infrastructure.
- Cost Savings: By eliminating the need for on-premises hardware and infrastructure maintenance, cloud computing networks can significantly reduce IT costs, including hardware purchases, maintenance, and energy consumption.
- Flexibility and Accessibility: Cloud computing networks provide users with the flexibility to access applications and data from any location with internet access, enabling remote work, collaboration, and productivity.
- Reliability and Redundancy: Cloud computing networks offer high levels of reliability and redundancy, with multiple data centers and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous availability of services and data.
- Security: Cloud computing networks implement advanced security measures, including encryption, access controls, and security monitoring, to protect data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Cloud computing networks handle software updates and maintenance tasks automatically, ensuring that users have access to the latest features and security patches without the need for manual intervention.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud computing networks offer built-in disaster recovery and backup solutions, allowing businesses to quickly recover data and applications in the event of a disaster or outage.
- Improved Performance: Cloud computing networks leverage distributed computing resources and advanced caching mechanisms to deliver improved performance and faster access to applications and data.
- Resource Optimization: Cloud computing networks enable organizations to optimize resource utilization by dynamically allocating computing resources based on workload requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: By leveraging cloud computing networks, businesses can rapidly deploy new applications and services, experiment with new ideas, and innovate more quickly, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of cloud computing networks are undeniable, organizations must also consider several challenges and considerations:
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Organizations must ensure that data stored and processed in the cloud complies with relevant regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Vendor Lock-In: Organizations that rely heavily on a single cloud provider may face challenges if they need to migrate data or applications to another provider in the future.
- Security Risks: While cloud providers implement robust security measures, organizations must still take steps to secure their data and applications in the cloud, including implementing encryption, access controls, and security monitoring.
- Performance and Latency: Organizations with stringent performance requirements may face challenges related to network latency and performance variability when accessing cloud-based resources over the internet.
- Cost Management: While cloud computing networks offer cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure, organizations must carefully manage their cloud spending to avoid unexpected costs and overspending.
Future Trends and Outlook
Looking ahead, several key trends are shaping the future of cloud computing networks:
- Edge Computing: Edge computing technologies are enabling organizations to process and analyze data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time decision-making capabilities.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing platforms abstract away infrastructure management tasks, allowing developers to focus on building and deploying applications without worrying about provisioning or managing servers.
- AI and Machine Learning: Cloud providers are increasingly integrating AI and machine learning capabilities into their services, enabling organizations to extract valuable insights from large volumes of data and automate decision-making processes.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is being integrated into cloud computing networks to enhance security, transparency, and trust in distributed systems, particularly in industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Key components of a cloud computing network include:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): This component provides virtualized computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis. Users can deploy and manage virtualized resources to build and run their own applications and services.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offerings provide a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexity of managing underlying infrastructure. PaaS services typically include development tools, middleware, and runtime environments.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS applications are fully hosted and managed by cloud service providers, allowing users to access software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Examples of SaaS applications include email, collaboration tools, and customer relationship management (CRM) software.
- Public Cloud: Public cloud services are provided by third-party cloud service providers and are accessible to users over the internet. Public cloud offerings are shared among multiple users and offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Private Cloud: Private cloud environments are dedicated to a single organization and are hosted either on-premises or by a third-party cloud provider. Private clouds offer enhanced security, control, and customization options compared to public clouds.
- Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud environments combine public and private cloud resources, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both deployment models. Hybrid clouds enable seamless data and workload migration between on-premises and cloud environments.
- Multi-Cloud: Multi-cloud strategies involve using multiple cloud service providers to meet different business requirements and avoid vendor lock-in. Multi-cloud architectures offer redundancy, resilience, and flexibility by distributing workloads across multiple cloud platforms.
- Cloud Networking: Cloud networking refers to the networking infrastructure and services that enable communication and connectivity within and between cloud environments. Cloud networking technologies include virtual networks, load balancers, firewalls, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Security and Compliance: Security and compliance are critical considerations in cloud computing networks. Cloud providers implement various security measures such as encryption, access controls, and security monitoring to protect data and infrastructure from cyber threats and ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Scalability and Elasticity: Cloud computing networks offer scalability and elasticity, allowing organizations to quickly scale resources up or down based on demand. This enables businesses to optimize resource utilization, accommodate fluctuating workloads, and support growth without the need for significant upfront investments in infrastructure.
Cloud computing networks represent a paradigm shift in how organizations deploy, manage, and utilize computing resources. With their unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency, cloud computing networks are empowering businesses to innovate, compete, and thrive in today’s digital economy. By understanding the fundamental principles, components, benefits, challenges, and future trends of cloud computing networks, organizations can harness the full potential of this transformative technology to drive growth and success.


