In recent years, cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate, revolutionizing how they store, manage, and access data and applications. By leveraging cloud-based services, organizations of all sizes can streamline their operations, increase efficiency, and drive innovation. In this article, we’ll explore the top 10 benefits of cloud computing and how they can empower businesses to thrive in today’s digital landscape.
1. Cloud Computing Cost Savings:
One of the most significant benefits of cloud computing is its potential to reduce IT costs. Traditional on-premises infrastructure requires substantial upfront investments in hardware, software, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand and only pay for what they use. This eliminates the need for costly hardware upgrades and maintenance, resulting in significant cost savings over time.
2. Scalability and Flexibility Cloud Computing
One of the primary benefits of cloud computing is its unparalleled scalability and flexibility. Unlike traditional on-premises infrastructure, cloud platforms allow businesses to scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Whether it’s handling sudden spikes in traffic or accommodating growth, cloud solutions provide the agility needed to adapt quickly to changing business requirements.
3. Flexibility and Accessibility:
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its accessibility. With cloud-based services, users can access data and applications from any internet-enabled device, anytime, anywhere. Whether it’s accessing files on a smartphone during a business trip or collaborating on a project from a remote location, cloud computing provides unparalleled flexibility and convenience, empowering users to stay productive on the go.
4. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities, helping businesses mitigate the risk of data loss and downtime. Cloud-based backup and recovery solutions replicate data across multiple redundant servers and geographically dispersed data centers, ensuring data availability and resilience in the event of hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. With cloud-based disaster recovery solutions, businesses can minimize downtime, maintain continuity of operations, and protect critical business assets.
5. Improved Security:
Security is a top priority for businesses, especially when it comes to protecting sensitive data and confidential information. Contrary to common misconceptions, cloud computing offers robust security features and compliance certifications that meet or exceed those of traditional on-premises infrastructure. Cloud service providers invest heavily in state-of-the-art security measures, including encryption, access controls, and threat detection, to safeguard data against unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats. By leveraging cloud-based security solutions, businesses can enhance their overall security posture and minimize security risks.
6. Enhanced Collaboration:
Cloud computing fosters collaboration and teamwork by providing centralized access to shared resources and collaborative tools. Cloud-based productivity suites, such as G Suite and Microsoft 365, enable real-time collaboration on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations, allowing multiple users to edit and collaborate simultaneously from anywhere. Additionally, cloud-based project management and communication tools facilitate seamless collaboration among remote teams, enabling efficient task management, communication, and collaboration across different departments and locations.
7. Increased Agility and Innovation:
Cloud computing accelerates innovation by providing businesses with the agility and flexibility to experiment, iterate, and deploy new applications and services rapidly. With cloud-based development platforms and tools, developers can access a wide range of resources, frameworks, and services to build, test, and deploy applications more efficiently. This agility enables businesses to respond quickly to market changes, customer feedback, and emerging trends, driving continuous innovation and competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced digital economy.
8. Centralized Management and Automation:
Cloud computing simplifies IT management and operations by centralizing infrastructure, applications, and services in a unified cloud environment. Cloud management platforms and automation tools enable businesses to provision, configure, and manage resources more efficiently, reducing manual overhead and streamlining IT operations. By automating routine tasks and workflows, businesses can free up IT resources to focus on strategic initiatives and innovation, improving overall efficiency and productivity.
9. Eco-Friendly and Sustainable:
Cloud computing offers environmental benefits by reducing the carbon footprint and energy consumption associated with traditional on-premises infrastructure. Cloud data centers are designed for energy efficiency and utilize advanced cooling and power management technologies to optimize energy usage. By leveraging cloud-based services, businesses can minimize the need for on-premises hardware, which reduces energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and electronic waste. Additionally, cloud providers increasingly invest in renewable energy sources to power their data centers, further enhancing their sustainability credentials.
10. Global Reach and Market Expansion:
Cloud computing enables businesses to expand their reach and enter new markets more easily by providing access to a global network of data centers and resources. With cloud-based services, businesses can deploy applications and services closer to their customers, reducing latency and improving performance for users worldwide. Additionally, cloud computing facilitates compliance with local data privacy and regulatory requirements, enabling businesses to expand into new geographic regions while maintaining regulatory compliance. By leveraging cloud-based infrastructure and services, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, expansion, and market reach on a global scale.
Cloud computing offers a myriad of benefits that empower businesses to innovate, collaborate, and thrive in today’s digital economy. From cost savings and scalability to flexibility and security, the advantages of cloud computing are clear. By embracing cloud-based solutions and leveraging the power of the cloud, businesses can drive efficiency, agility, and innovation while staying competitive in an increasingly interconnected and fast-paced world.
Unveiling the Power of Cloud Computing: A Comprehensive Guide
In recent years, cloud computing has emerged as a transformative force reshaping the landscape of technology and business. From startups to multinational corporations, organizations of all sizes and industries are leveraging cloud computing to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and drive innovation. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of cloud computing, its key components, deployment models, benefits, and emerging trends shaping the future of the cloud.
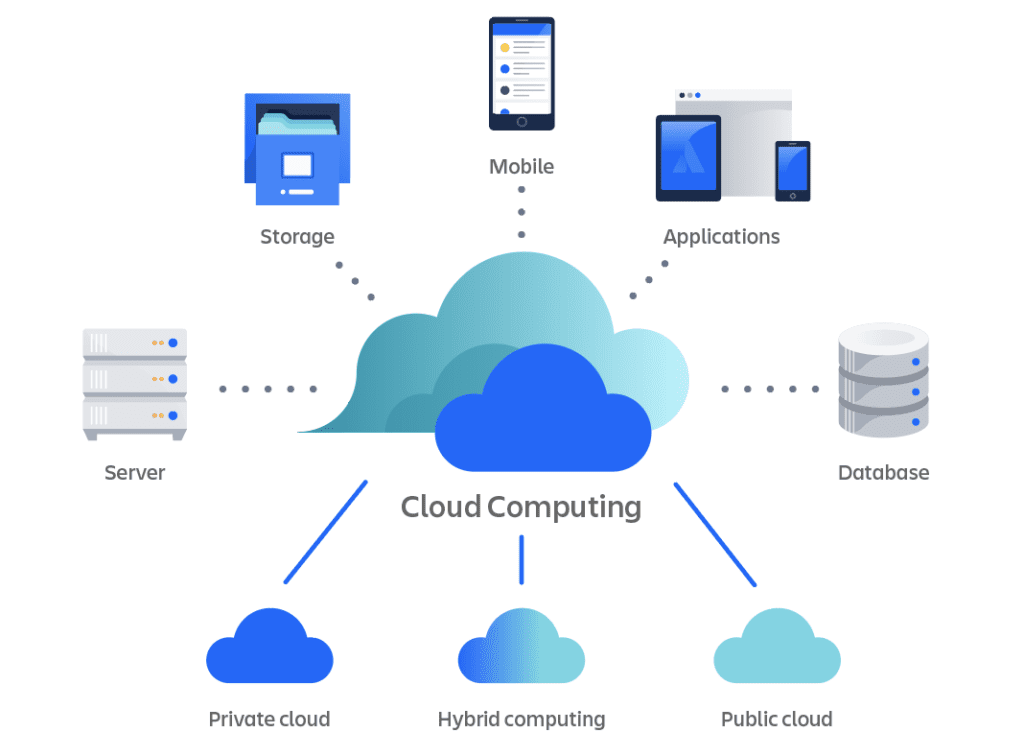
Understanding Cloud Computing:
At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, providing on-demand access to a shared pool of resources, including servers, storage, networking, databases, applications, and more. Unlike traditional on-premises infrastructure, where organizations manage and maintain their own hardware and software, cloud computing enables users to access and utilize computing resources hosted and managed by third-party cloud service providers.
Key Components of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing encompasses several essential components, each playing a distinct role in delivering cloud services:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure. Users can leverage IaaS to deploy and manage their own virtualized environments without the need for physical hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the complexity of infrastructure management. PaaS providers offer development frameworks, runtime environments, and deployment tools to streamline the application development process.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, and update software locally. Popular examples of SaaS applications include email, collaboration tools, customer relationship management (CRM), and productivity suites.
Deployment Models of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing offers several deployment models, each catering to different organizational needs and preferences:
Public Cloud: Public cloud services are hosted and managed by third-party cloud providers and made available to the general public over the internet. Public cloud environments offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for startups, small businesses, and organizations with dynamic workloads.
Private Cloud: Private cloud environments are dedicated to a single organization and hosted either on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer greater control, security, and customization options compared to public clouds, making them suitable for enterprises with stringent security and compliance requirements.
Hybrid Cloud: Hybrid cloud environments combine elements of public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds while retaining control over sensitive data and applications in private clouds. Hybrid clouds enable seamless integration and workload portability across multiple environments, providing flexibility and agility for businesses with diverse requirements.
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing offers a multitude of benefits for organizations seeking to modernize their IT infrastructure and drive digital transformation:
Cost Efficiency: Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront capital investments in hardware and infrastructure, reducing IT costs and enabling organizations to pay only for the resources they consume on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Scalability: Cloud computing offers virtually unlimited scalability, allowing organizations to quickly scale resources up or down to accommodate fluctuations in demand, without the need for additional hardware or infrastructure investments.
Flexibility and Agility: Cloud computing provides unparalleled flexibility and agility, enabling organizations to rapidly deploy, scale, and manage applications and services to meet evolving business needs and market demands.
Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud-based collaboration tools and platforms facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among remote teams, enabling real-time collaboration on documents, projects, and workflows from anywhere with an internet connection.
Improved Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in state-of-the-art security measures, including encryption, access controls, and threat detection, to safeguard data and applications against cyber threats and breaches, often providing greater security than traditional on-premises environments.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud-based backup and disaster recovery solutions enable organizations to replicate data and applications across geographically dispersed data centers, ensuring data availability and resilience in the event of hardware failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage: Cloud computing accelerates innovation by providing organizations with access to cutting-edge technologies, development tools, and resources to experiment, iterate, and deploy new applications and services rapidly, driving competitive advantage and differentiation in the market.
Environmental Sustainability: Cloud computing offers environmental benefits by reducing the carbon footprint and energy consumption associated with traditional on-premises infrastructure, as cloud data centers are designed for energy efficiency and utilize renewable energy sources.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing:
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of cloud computing and driving innovation in the industry:
Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computing resources closer to the point of data generation, enabling real-time processing and analysis of data at the network edge, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements for applications and services.
Serverless Computing: Serverless computing abstracts infrastructure management and allows developers to focus on writing code without the need to provision or manage servers. Serverless platforms automatically scale resources based on demand, providing cost-effective and efficient execution of code.
Multi-Cloud and Interoperability: Organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies to leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers and avoid vendor lock-in. Interoperability standards and tools enable seamless integration and workload portability across diverse cloud environments.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Cloud providers are integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities into their services to enable advanced analytics, predictive insights, and automation, empowering organizations to derive actionable intelligence from data and drive innovation.
Cloud computing represents a paradigm shift in how organizations consume, deploy, and manage IT resources, offering unprecedented agility, scalability, and innovation for businesses of all sizes and industries. By embracing cloud computing, organizations can modernize their IT infrastructure, drive digital transformation, and gain a competitive edge in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.